What is Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition in which the body is unable to properly regulate the amount of sugar in the blood. This can lead to a range of health problems, including heart disease, nerve damage, and kidney disease. There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. In type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce enough insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. In type 2 diabetes, the body does not produce enough insulin or the cells in the body do not effectively use the insulin that is produced. Treatment for diabetes typically involves managing blood sugar levels through a combination of medication, diet, and exercise.
Diabetes is a chronic condition, meaning that it can last for a long time and can have a range of harmful effects on the body. If left untreated, diabetes can lead to a range of complications, including heart disease, nerve damage, and kidney disease. In some cases, high blood sugar levels can also cause dizziness, blurred vision, and fatigue.
There are several medications that can be used to treat diabetes. The type of medication that is used will depend on the type of diabetes that a person has and their individual needs. For example, people with type 1 diabetes may need to take insulin injections to help regulate their blood sugar levels. People with type 2 diabetes may be prescribed medications that help the body produce more insulin or that make the cells more sensitive to insulin. These medications can be taken orally or by injection. It is important for people with diabetes to work closely with their healthcare providers to determine the best treatment plan for their individual needs.
Top 10 food habits that can help manage diabetes
1. Below are some top food habits that can help manage diabetes:
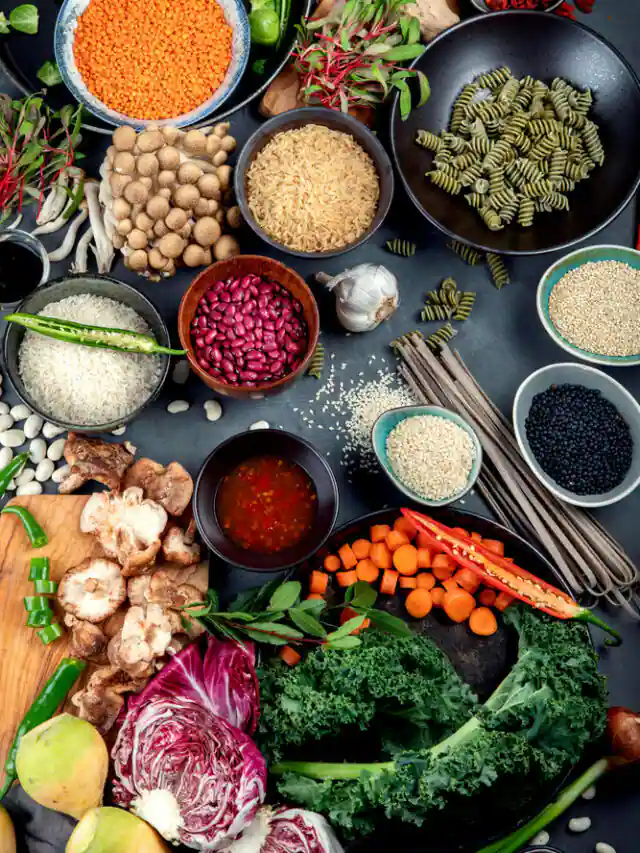
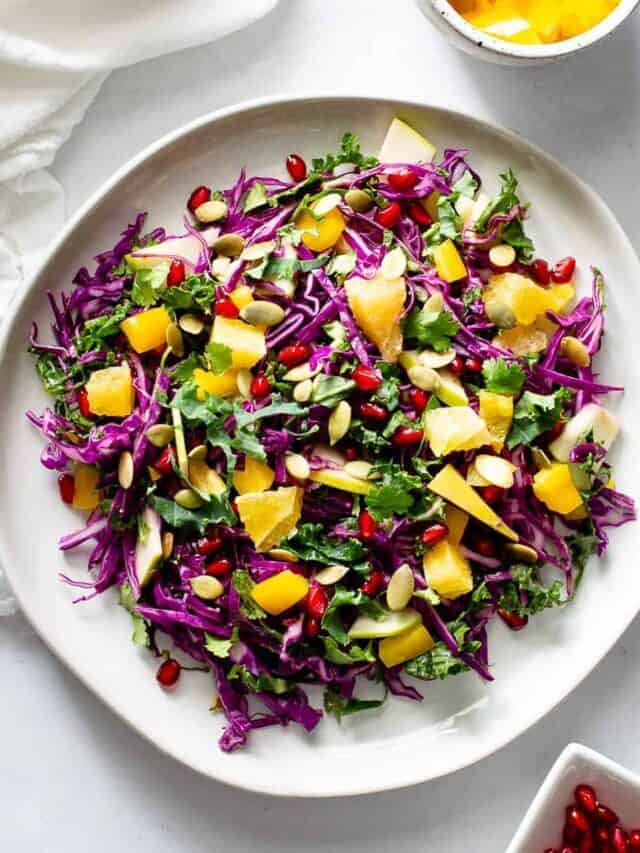
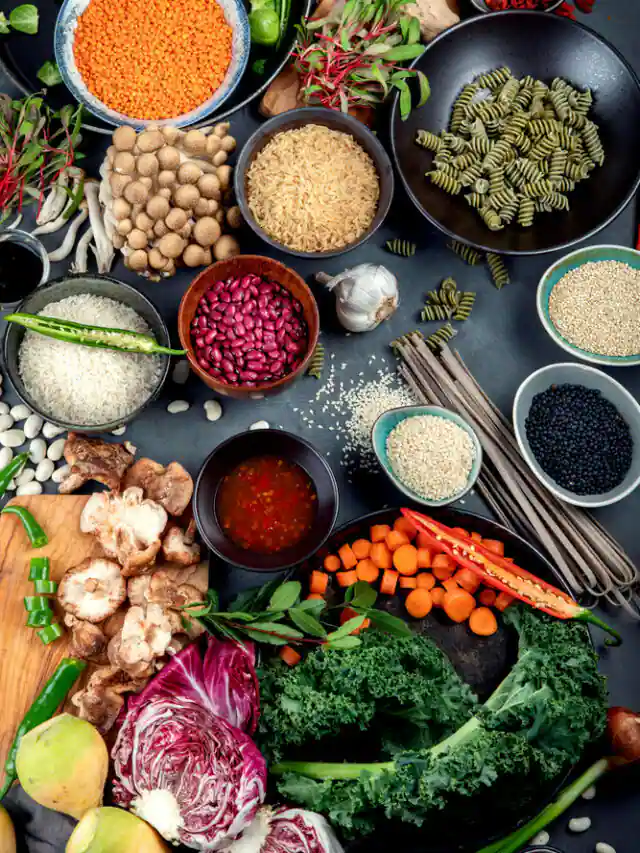
2. Eat a healthy and balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean protein sources, and healthy fats.
3. Choose foods that are low in added sugars, salt, and unhealthy fats.
4. Limit your intake of processed and packaged foods, as well as foods that are high in saturated and trans fats.
5. Eat regular meals and snacks throughout the day to help manage your blood sugar levels and avoid large fluctuations.
6. Be mindful of your portion sizes and aim to eat only until you are satisfied, rather than overfull.
7. Try to include some physical activity in your daily routine, such as walking or biking, to help control your blood sugar levels.
8. Consider incorporating low-glycemic index foods into your diet, which can help to slow the release of sugar into the bloodstream and improve blood sugar control.
9. Try to limit your intake of alcohol, as it can interfere with blood sugar control and increase your risk of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia).
10. If you take medication to manage your diabetes, be sure to take it as prescribed and follow your healthcare provider’s instructions.
Consider working with a registered dietitian or certified diabetes educator who can help you develop a meal plan that is tailored to your individual needs and goals.